Product
Research
What is product research?
Product research let you understand what customers really want, allowing you to tailor your product offering to meet their needs and giving you a real competitive edge.
New product research helps you refine product designs and plans before committing yourself to expensive product development costs. Whilst continuing product testing and research can drive in As the new product development process continues, product research helps you identify the key factors that matter to customers – showing you what to focus on. Product research can be linked with other aspects of marketing. For example, it can help you assess how much customers might be willing to pay for new product features. Research can also be used to assess other aspects of product design, such as product packaging or brand name.
Concept testing for new products can be very challenging – the way people react to new products in theory can be very different from the reality. Customers may say they like a new idea, but in reality show reluctance to switch to new products or decide that it is not worth the price.
TYPES OF PRODUCT TESTING:
1) Monadic testing.
2) Sequential monadic testing
3) Paired- comparison testing
4) Protomonadic testing.
Ways of conducting product testing:
In-house Usage Test
On IHUT studies, products are getting shipped to the target audience where the research is conducted within consumers’ homes.
o Consumers prepare and consume the product within their homes and share their experiences during and after the experimentation.
o IHUTs are getting conducted via mobile/online market research platforms, companies.
Central Location Test
For CLT studies, consumers are getting recruited to participate in research within controlled environments.
o These controlled environments can be a mall or a laboratory, where consumers come to these places to consume a product or use it, then share their experiences.
o CLTs are getting conducted via traditional market research companies.
o CLT offers the specialized advantage over face to face interviewing. The response rates are fairly high and better results in cases of extremely long or difficult to survey.
o This method allows clients to directly observe interviewing, provide greater confidentiality than other research methods, and will not be impeded by pending legislation that will narrow the ability to recruit respondents.
Product Clinics
At a clinic products or prototypes can be tested in their competitive environment. “Clinic” here means that the participants approach the product in a central test.
Clinics are conducted at different times for different purposes. The design and makeup of these clinics vary. The most common purposes are:
o Evaluate and learn how to improve new models/products.
o Product clinics is product line planning, or product line optimization, where all the different models of one brand are displayed and evaluated.
o Price optimization, where consumers view the model/products within a class of vehicles/products, and then participate in choice modelling experiments.
o To set the stage for volumetric forecasting of sales.
Some clinics emphasize marketing positioning, while others are more human factor or design oriented, depending on the product development stage.
The engineering-focused clinics are often conducted on relatively recent product introductions to better understand early customer experiences. Owners describe both problems and delights with their vehicles to assist in product improvements.
Some clinics measure feature usability, desirability and pricing interest, from current to advanced features.
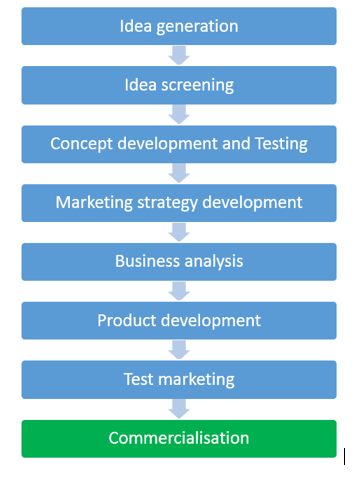
STEPS FOR PRODUCT TESTING
BENEFITS:
1) Achieve product superiority
2) Improve product performance and customer satisfaction
3) Monitor the potential threat levels
4) Cost reduction product formulation
5) Shelf life studies
6) The effects of price, brand name, or packaging upon perceived product performance.
7) Guidance to research and development in creating new products or upgrading existing products.
8) Monitoring the product quality
9) Predict customer acceptance of new products
10) Gives a product the chance to sell itself.
11) Helps in getting a competitive edge against similar products
12) Helps in receiving critical feedback about the product
13) Risk of a full scale launch is eliminated
